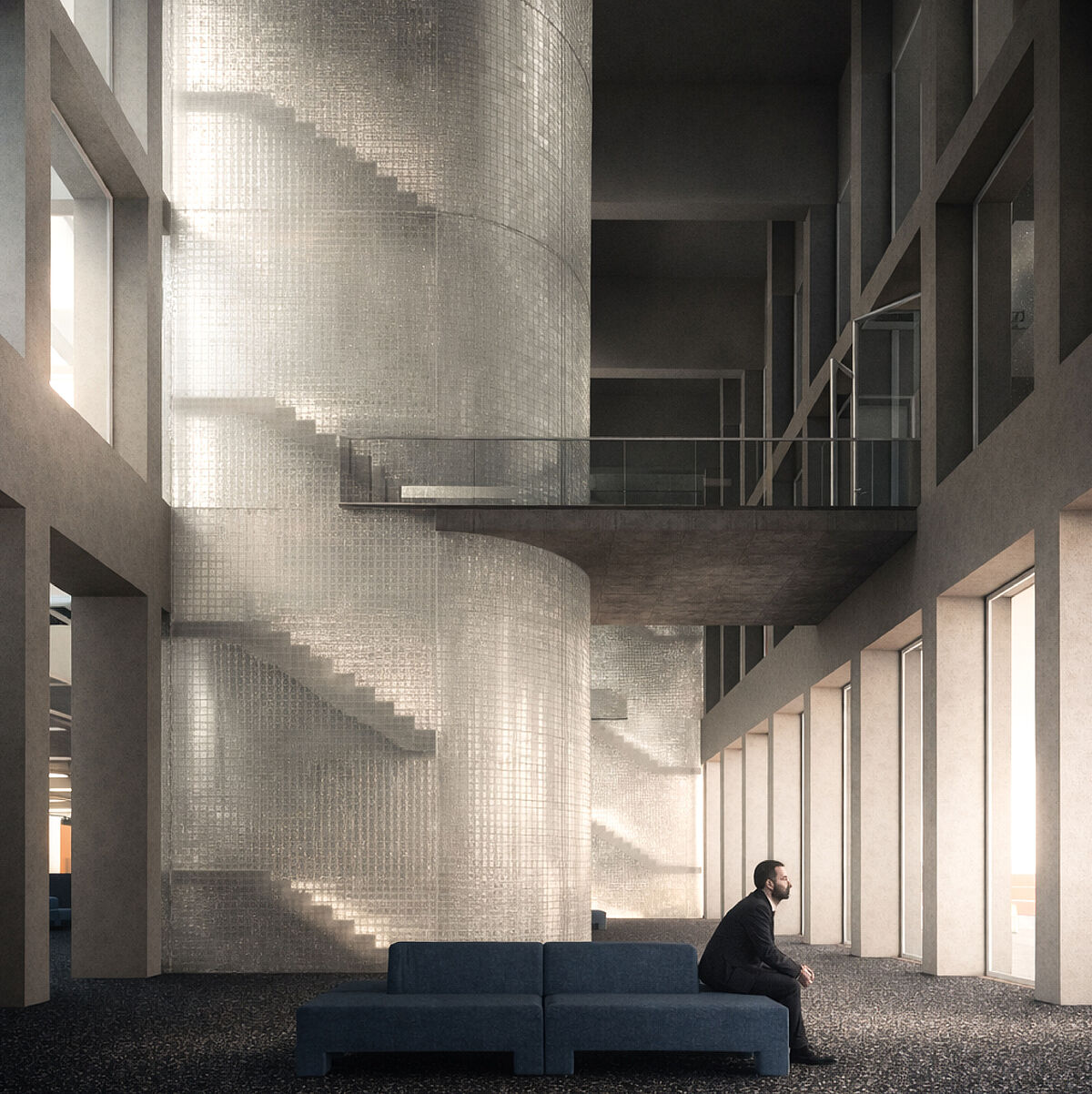
Urban Voids as Hidden Resources
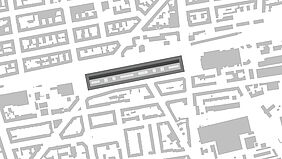
Urban voids are spaces within cities that have lost their original function or were never fully integrated into the urban structure. These include brownfields, abandoned industrial areas, leftover spaces between infrastructures, and isolated urban islands. Although often perceived as empty or problematic, urban voids represent valuable residual resources with strong potential for sustainable urban transformation.
Brownfields and Sustainable Urban Development
Brownfields are a key example of urban voids. They are frequently located in strategic positions close to city centers, transport networks, or waterfronts, yet remain unused due to contamination, unclear ownership, or economic uncertainty. In the context of climate change, housing shortages, and social inequality, the redevelopment of these sites is becoming increasingly important. Reusing existing urban land offers a more resource-efficient alternative to outward urban expansion.
Artificial Intelligence as an Analytical and Planning Tool
Artificial intelligence introduces new possibilities for analyzing and activating urban voids. By processing large datasets related to land use, mobility patterns, environmental conditions, and social behavior, AI can reveal hidden potentials that are often overlooked by conventional planning approaches. In addition, AI-based simulations allow different redevelopment scenarios to be tested and evaluated in terms of their environmental, social, and economic impacts.
Adaptive Design and Participatory Processes
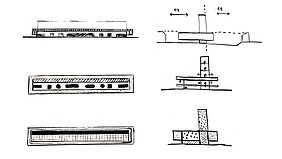
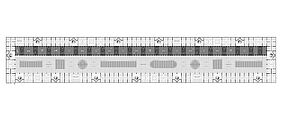
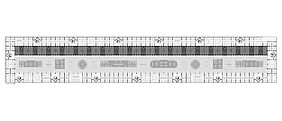
Due to their complex histories and fragmented structures, urban voids require flexible and adaptive design strategies. AI-driven design tools can generate multiple spatial scenarios, optimize layouts, and respond to changing conditions over time. At the same time, AI can support participatory planning by analyzing data from public surveys, social media, and citizen input. This enables the transformation of neglected urban spaces into active public areas, ecological corridors, or mixed-use developments, integrating urban voids as resilient and meaningful components of the urban fabric.